Declining consumer confidence signals economic uncertainty

The retail freight market is facing a complex situation, primarily driven by evolving tariff policies and their impact on consumer behavior. Current U.S. tariffs, especially those imposed on Chinese-manufactured goods, have far-reaching implications for the retail industry. The impact will vary across different retail channels, largely dependent on specific product assortments.
Divergent tariff focus areas
Analyzing the current tariff situation reveals three distinct areas of focus:
1. Mexico and Canada
Following the White House’s decision to maintain duty-free status for most goods that are compliant with the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) and clarification on tariffs impacting the retail sector, the retail trade relationship with Canada and Mexico appears to be in a stable state for the near future.
2. China
The trade trajectory with China remains distinct. The situation is currently the most difficult to anticipate, suggesting a unique and potentially more complex set of planning scenarios for retailers and retail suppliers.
3. The rest of the world
The coming weeks will be critical as the United States engages in negotiations regarding the country-by country reciprocal tariffs that were announced April 2, 2025, then lowered to 10% as bilateral trade talks began. The outcomes of these discussions will determine the future tariff implications for retail trade with these nations.
For more specifics around tariffs, visit the Government & Regulations page in this report.
Strategies for mitigating the impact of retail tariffs
Retailers are employing several strategies to combat increasing tariffs, including:
- Pausing orders or shipments from international vendors to reassess sourcing strategies
- Working with suppliers to lower prices to help offset increased costs imposed by tariffs
- Diversifying supply chain networks by exploring alternative countries for production needs
Declining consumer confidence and economic implications
A potential decline in consumer retail spending poses broad economic risks, potentially slowing U.S. economic growth and lowering the U.S. GDP forecast for 2025. Consumer confidence has already shown signs of weakening. The University of Michigan’s Index of Consumer Sentiment dropped 14.7 points in the first three months of 2025, reflecting growing economic uncertainty for the United States.
Retail inventory build-up evident in early 2025 import figures
Recent import data clearly indicated inventory was pulled forward in the first quarter of 2025 across various industries, including retail. Consumer goods imports specifically spiked in Q1. In January and February 2025 alone, total import values saw a substantial increase of nearly $128 billion compared to the same period in 2024 and preliminary March numbers were showing a continued increase in import values.
Real Imports of Consumer Goods, Except Food & Automotive
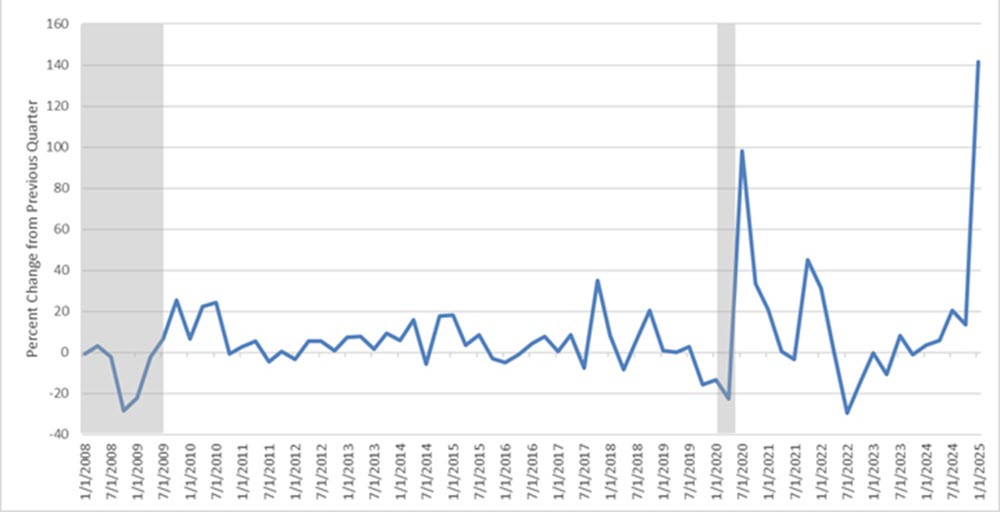
This surge included significant growth in consumer goods such as cell phones, textiles, apparel, and pharmaceuticals. The most significant surge across all imports was observed in finished metals, directly linked to an abnormal increase in gold imports in January that is adding to the finished metal shapes import values along with steel and aluminum.
YoY Change in Imports (by value, YTD 2025)
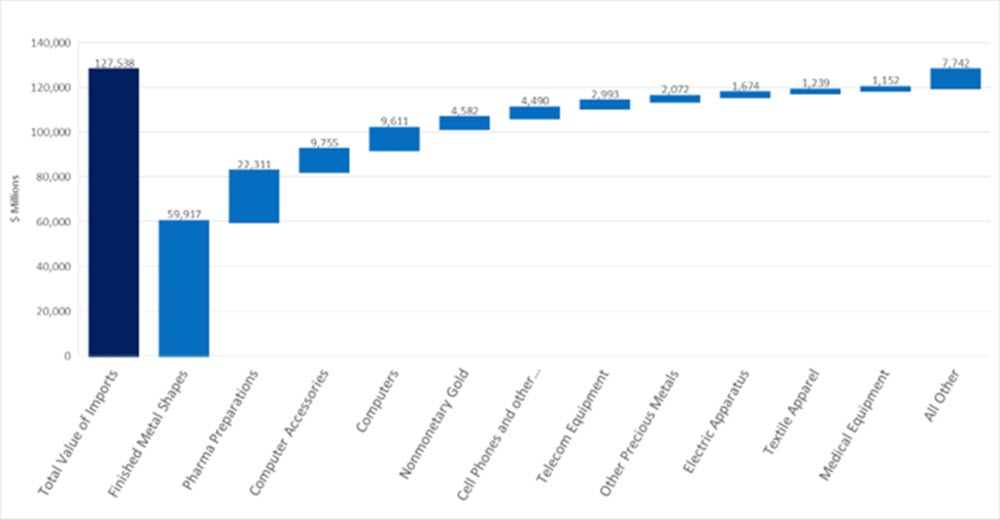
This proactive inventory management strategy suggests many companies anticipated the tariff implications and adjusted import strategies accordingly.
U.S. Imports of Good (by value, YTD)
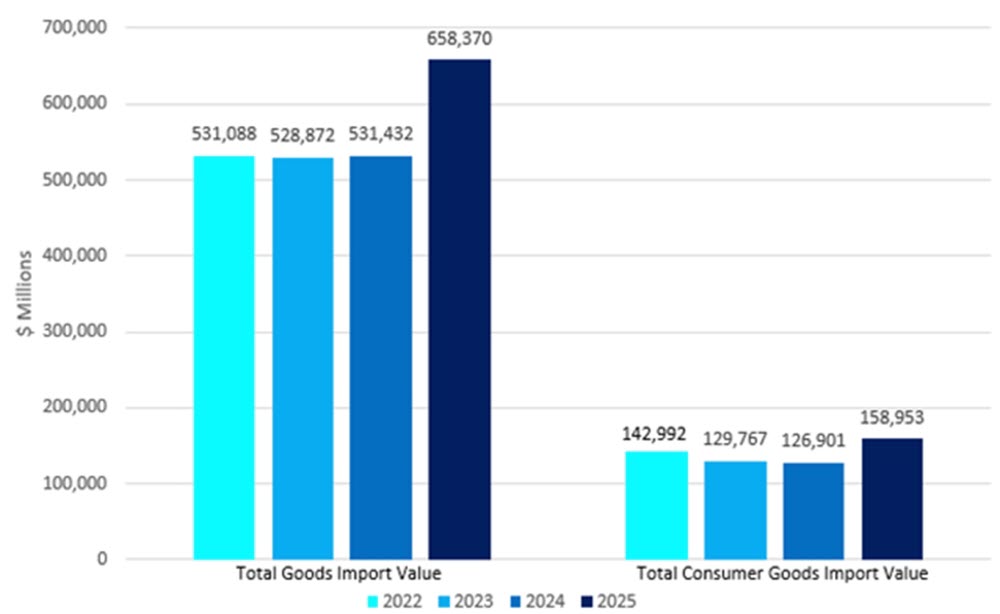
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, April release of U.S. International Trade in Good & Services